- Conditions
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome CTS
Introduction
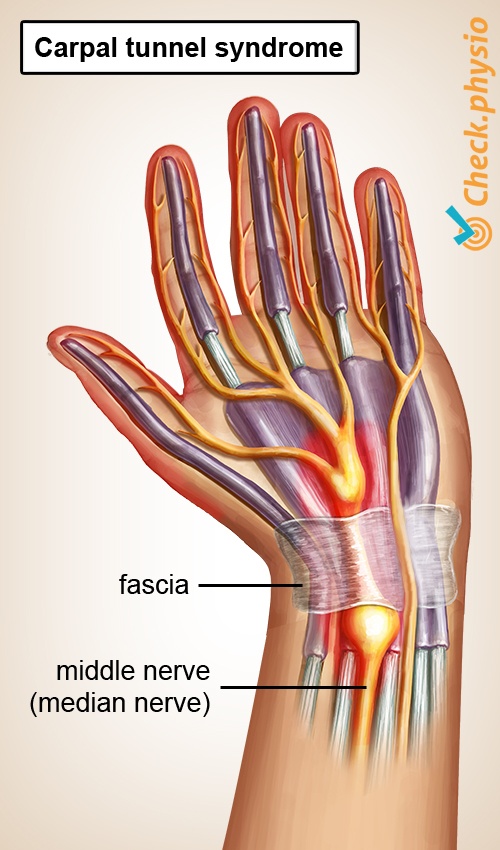
In carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), the middle nerve of the hand, which enters the hand from the forearm, is constricted in the wrist joint. This causes pain, pins and needles, tingling or numbness in the fingers and the palm of the hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is more common in people aged between 40 and 60. In addition, women, pregnant women and people with rheumatoid arthritis or obesity are at increased risk of developing the symptoms.
Description of condition
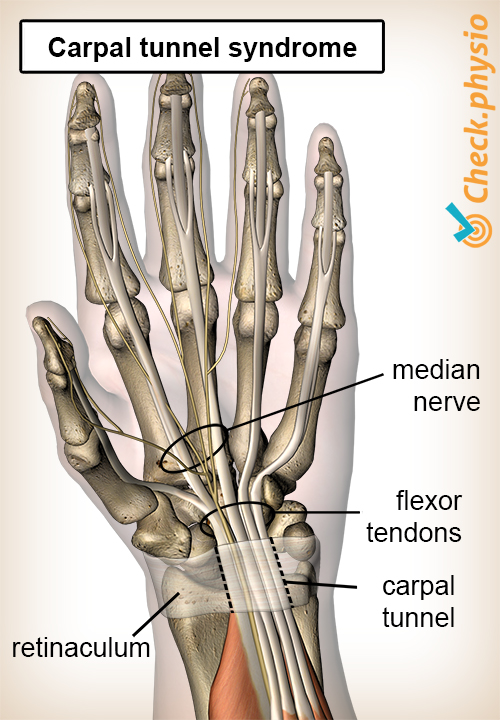
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passage for nerves and tendons running from the forearm to the hand. The tunnel is formed by the carpal bones and a sturdy tendon ligament (also called retinaculum) that is located along the front of the wrist joint.
The middle nerve of the hand - the median nerve - runs through this tunnel. Sometimes the tunnel can become too narrow, causing the median nerve to become constricted. This causes symptoms in the hand, which we call carpal tunnel syndrome.
Cause and history
Frequent and repetitive movements of the hand, awkward working positions and mechanical vibrations to the hand/arm can cause these symptoms.
Signs & symptoms
- Pain, pins and needles or numbness in the fingers and the palm of the hand. The little finger may remain free of symptoms.
- Loss of sensation and/or loss of strength in the hand.
- Nocturnal symptoms.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis can be made based on the patient's story and the location of the symptoms. There are a number of tests that can support a suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome.
A nerve conduction test (EMG) may be used to examine the functioning of the nerves. This is done using small electrical pulses. An EMG generally only has added value if a surgical procedure is being considered.
Treatment and recovery
A quarter of all cases show a spontaneous reduction in symptoms within a year. There are a number of treatment options:
- Medical taping. Elasticated tape over the carpal tunnel.
- Splint treatment. The wrist is fixed in a neutral position at night and whenever possible during the day. This should reduce the symptoms within four weeks.
- Controlled traction (literally: pulling) of the forearm and wrist using a traction device to relax the structures involved in the symptoms continuing.
- Corticosteroid injection (anti-inflammatories) in or surrounding the carpal tunnel.
- Surgical severing of the fascia, to increase the space in the carpal tunnel and reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Exercises
Follow the exercise program with exercises for carpal tunnel syndrome.
More info
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your locality.
References
Peters-Veluthamaningal, C., Willems, W., Smeets, J.G.E., Windt, D.A.W.M. Van der, Spies, M.N., Strackee, S.D., Vos, K., Wind, L.A. & Geraets, J.J.X.R. (2010) NHG-Standaard. Hand- en polsklachten Huisarts Wet. 2010:53(1):22-39.
Nugteren, K. van & Winkel, D. (2006) Onderzoek en behandeling van de hand - het pols gewricht Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Cleland, J.A. & Koppenhaver, S. (2011) Netter's orthopaedic clinical examination: an evidence-based approach 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier.