- Conditions
- Posterior ankle impingement
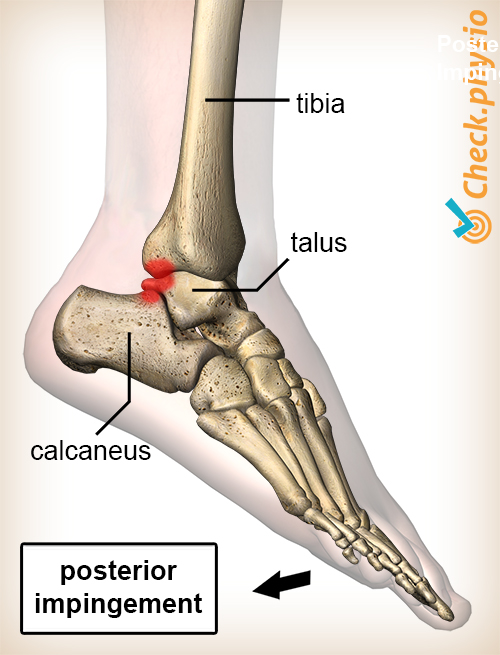
Posterior ankle impingement Tissue getting trapped at the back of the ankle joint
Introduction
Posterior ankle impingement involves pain behind the ankle. The pain is caused by trapped structures. These structures generally become trapped during movements in which the ankle is extended.
Because a posterior ankle impingement is difficult to detect, the symptoms often persist for a long time before a diagnosis is made.
Other names for this condition are: posterior ankle impingement syndrome, talar compression syndrome, os trigonum syndrome, nutcracker syndrome, posterior blockage of the ankle.
Description of condition
An impingement at the back of the ankle joint means that the structures at the back of the ankle joint become trapped during movement. These structures may be soft tissue (for example capsules, ligaments and tendons) or a bone spur or a loose bone fragment.
Posterior ankle impingement is defined as something being trapped between the rear of the tibia and the rear of the heel bone (the calcaneus). Different structures may become trapped between these bony structures:
- The ankle bone (the talus).
- Joint capsules and/or ligaments.
- The tendon of a muscle (particularly the m. flexor hallucis longus).
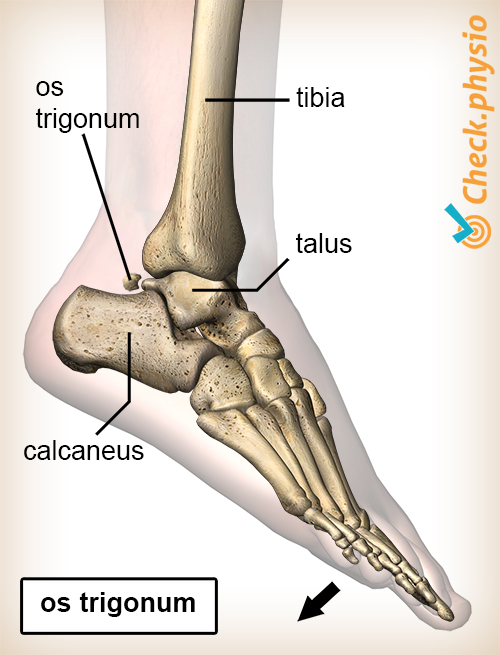
- An os trigonum.This is an anatomical abnormality that occurs in 2% of the population. There is an extra bone fragment present behind the ankle bone.
An os trigonum is found to be the cause of a posterior impingement relatively frequently.
As with anterior ankle impingement, a distinction is made between impingement of bone structures and impingement of soft tissue. A combination of these two types of impingement is often seen.
Cause and history
Posterior ankle impingement can occur acutely, for example, as a result of a forced movement of the ankle with the foot moving downward. Sometimes a fracture can then occur.
The symptoms can also be caused by strain. When there is repeated mild impingement, this can cause a little bit of damage each time. We call this microtrauma. If microtrauma occurs in the joint over a longer period of time, the damaged structures may eventually start to cause symptoms.
Posterior impingement due to strain is mainly seen in sports where the foot frequently moves downward. This includes ballet dancers, soccer players and runners. The extended position of the foot may cause compression of the structures between the heel bone and the tibia.
Impingement can also occur with chronic instability of the ankle. This means that the ankle is no longer able to keep itself stable with help from the surrounding muscles and ligaments. Due to the lack of control in the joint, impingement can occur more easily. Chronic instability is often seen after ankle sprains.
People who have an os trigonum have had it since birth. The size of this bone fragment may vary. If the os trigonum is naturally larger, it may become trapped without any other cause such as instability, strain, an accident or a sprained ankle.
Signs & symptoms
The pain is located mainly at the back of the ankle and is sometimes felt inside the ankle. If bone structures are trapped, the pain is usually felt at the back and on the outside.
During the physical examination, tenderness is felt at the back of the ankle. The downward movement of the foot may provoke the symptoms. The mobility of the ankle joint is normal in many cases.
- Pain at the back of the ankle.
- The pain has often been present for a long time (several months).
- Moving the foot completely downward is painful.
- Sometimes, local swelling is present.
- Pain may be provoked when jumping because this makes the foot extend completely.
Diagnosis
Because many different disorders can occur at the back of the ankle, it is difficult to make a correct diagnosis. As a result, many patients often walk around for months with these symptoms.
There are few good tests that make it easy to diagnose posterior ankle impingement. The diagnosis is therefore made on the basis of the patient's story, provoking (pressure) pain at specific points and pain during forced ankle movements.
Because many different disorders are possible, medical imaging is often used to rule out or detect certain disorders. It is also easier to determine the type of impingement in this way.
Treatment and recovery
If a posterior impingement of the ankle is suspected, the cause of the symptoms is reviewed. If these are suspected to have arisen from instability of the ankle joint or strain, conservative therapy through physiotherapy is the correct treatment. The treatment will then consist of mobilizing the joint, exercise therapy and, in particular, rest and adjustment of the sporting activity. This is mainly to avoid incorrect movements and/or overextension of the ankle.
In a soft tissue impingement, the results of conservative treatment are generally better than in an impingement of bony structures. If impingement of a bony structure is suspected, surgery may be considered. It will usually be reviewed first whether the provoking movements can be avoided. This will often already result in a reduction of symptoms, making an operation unnecessary.
Athletes who cannot avoid the provoking movements (e.g. top athletes) will undergo a surgical intervention. Surgery will also be performed if there is a loose bone fragment in this region.
Exercises
Follow the exercise program with exercises for posterior ankle impingement.
More info
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your locality.
References
Amerongen, I.A. van & Cingel, R.E.H. van (2015) Het posterieur enkel impingement syndroom. Een beschrijvende review Sport & Geneeskunde. Juli-2015-2.